Innovative Paper-Thin Batteries: A Sustainable Future
Written on
Chapter 1: Introduction to Biodegradable Batteries
Recent advancements in technology highlight the importance of enhancing existing innovations rather than solely creating new ones. A significant breakthrough reported in Advanced Science reveals that researchers have developed biodegradable zinc batteries, comparable in size to a water biscuit. These batteries present a promising solution in the quest for environmental sustainability, especially as the demand for smartphones, laptops, and other smart devices continues to grow in today's world.
These batteries provide a more eco-friendly alternative. Their non-toxic nature, coupled with the absence of plastic or aluminum casings, allows for safe disposal—simply bury them underground after use.
Section 1.1: Characteristics of the New Batteries
The newly designed batteries are smaller than traditional options, enabling greater usage without complications. Developed at Nanyang Technological University in Singapore, these innovative batteries feature electrodes that are "sandwiched" between layers of cellulose paper, which are screen-printed on both sides and reinforced with hydrogels.
Subsection 1.1.1: The Composition of the Batteries
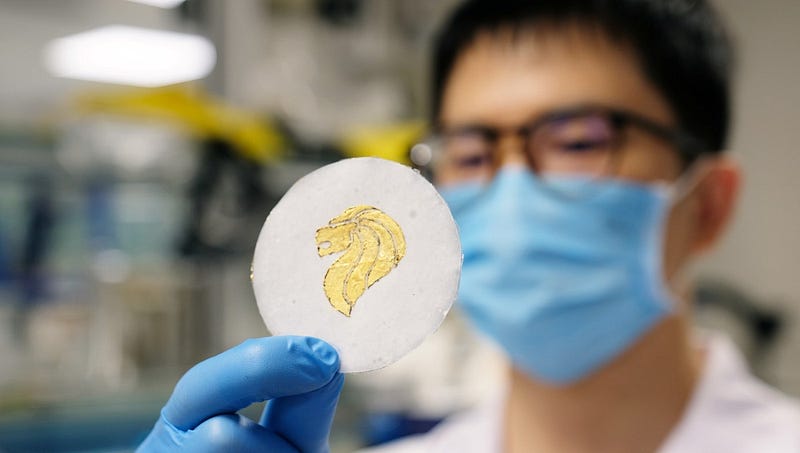
To create paper, cellulose fibers serve as the main binding agent, typically extracted from wood or related materials through chemical or mechanical processes. Depending on the extraction method and quantity used, cellulose paper can be both environmentally and economically sustainable.

Hydrogels, which act as a natural adhesive, reinforce the thin cellulose layers, filling in the gaps created by the fibers. These materials are commonly used in everyday products, such as contact lenses and hygiene items. When the battery reaches the end of its life, it can be buried and will decompose within about a month.
Section 1.2: Performance and Longevity
The study showcased the remarkable longevity of these batteries through experiments involving a square-shaped printed battery measuring 4 centimeters on each side (approximately 1.57 inches). This small battery powered a fan for about 45 minutes, showing no interruption even when twisted or bent. Furthermore, another square battery powered an LED light, remaining functional despite portions being removed.
Chapter 2: The Future of Sustainable Technology
Innovative technologies have the potential to help us tackle the pressing challenges of our time. Researchers suggest that these batteries could be seamlessly integrated into wearable or foldable smart devices, such as smartphones or health monitors, thereby enhancing convenience while contributing to environmental preservation.
As noted by science author Steven Johnson, “If you look at history, innovation doesn’t come just from giving people incentives; it comes from creating environments where their ideas can connect.”
For a deeper understanding of these breakthroughs, view the following videos:
Chinese scientists develop paper-thin batteries for electronic devices.
Biodegradable paper-thin batteries by NTU Singapore scientists.
For more intriguing insights, explore additional articles:
Scientists Develop a Life-Saving Snake-Shaped Battery
If successful, this innovation could significantly aid individuals with mobility challenges.
Malawi Innovator Single-Handedly Provides Free Electricity For His Whole Village
With no formal training, he emerged as the leading electrical engineer in his community.